The RGB (Red, Green, Blue) color model is an additive color model, meaning that when you mix these colors of light, you get white. It’s the basis for how digital screens display color.
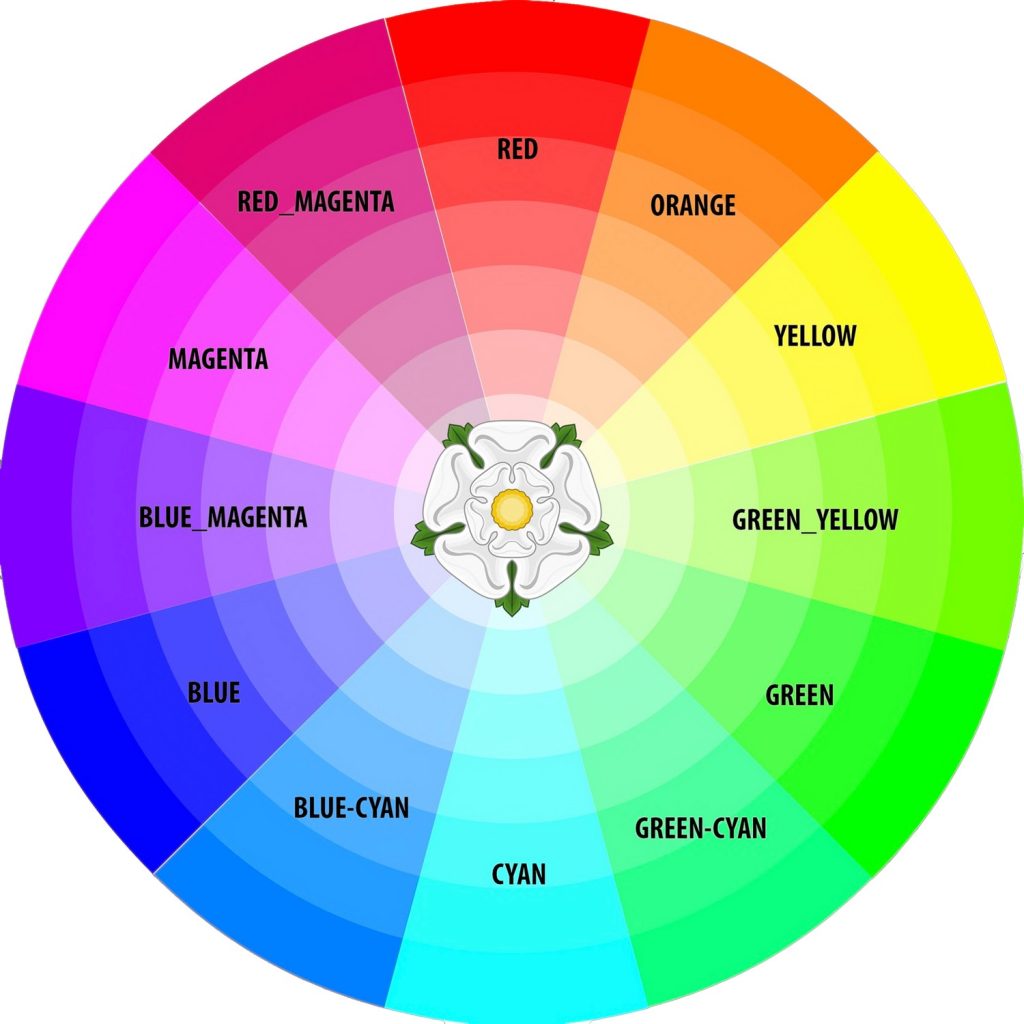
| Color Type | Color Name | Composition (RGB) |
| Primary Colors | Red | Pure Red |
| Green | Pure Green | |
| Blue | Pure Blue | |
| Secondary Colors | Yellow | Red + Green |
| Cyan | Green + Blue | |
| Magenta | Red + Blue | |
| Tertiary Colors | Orange | Red + Yellow (Red + Red + Green) |
| Green Yellow | Green + Yellow (Green + Red + Green) | |
| Green Cyan | Green + Cyan (Green + Green + Blue) | |
| Blue Cyan | Blue + Cyan (Blue + Green + Blue) | |
| Blue Magenta | Blue + Magenta (Blue + Red + Blue) | |
| Red Magenta | Red + Magenta (Red + Red + Blue) |
Export to Sheets
Note: The exact names and positions of tertiary colors can sometimes vary slightly depending on the specific color wheel representation, but these are common and logical based on the RGB mixing.
Various Types of Color Schemes
Color schemes are combinations of colors that are considered harmonious and visually pleasing. They are used to create specific moods and visual effects in photography and other visual arts.
- Monochromatic Color Scheme:
- Uses different tints, tones, and shades of a single hue.
- Example: Various shades of Blue (e.g., light blue, medium blue, dark blue). This creates a sense of unity, calm, or sophistication.
- Analogous Color Scheme:
- Uses colors that are next to each other on the color wheel. Typically involves 2-5 colors.
- Example: Green, Green Yellow, Yellow. This creates a harmonious and serene feel, often found in nature.
- Complementary Color Scheme:
- Uses two colors that are directly opposite each other on the color wheel. These create strong contrast and vibrancy.
- Example:
- Red and Cyan
- Green and Magenta
- Blue and Yellow
- This scheme creates a dynamic and eye-catching effect, making elements “pop.”
- Split-Complementary Color Scheme:
- Uses a base color and the two colors adjacent to its direct complement. This offers a high degree of contrast but is less jarring than a direct complementary scheme.
- Example: If you choose Red as your base color, its complement is Cyan. The split-complementary colors would then be Green Cyan and Blue Cyan.
- Triadic Color Scheme:
- Uses three colors that are equally spaced around the color wheel, forming an equilateral triangle. These schemes are vibrant and balanced.
- Example:
- Red, Green, Blue (the primary colors)
- Yellow, Cyan, Magenta (the secondary colors)
- Orange, Green Cyan, Blue Magenta
- Tetradic (Double Complementary) Color Scheme:
- Uses four colors arranged into two complementary pairs, forming a rectangle on the color wheel. This is the richest and most complex scheme, offering a wide range of possibilities but requiring careful balancing.
- Example: Red, Cyan, Green Yellow, Blue Magenta (Red-Cyan is one complementary pair, Green Yellow-Blue Magenta is another).
- Achromatic Scheme – Only an honorable mention really as this scheme is technically colorless, using only neutral grays, black, and white ! Classic, timeless, minimalist, and formal.
Understanding these color relationships allows photographers to make intentional choices that enhance their images, convey specific emotions, and create compelling visual narratives. A one page pdf detailing the various schemes may be downloaded here.
Full Color Reference (For Easy Copy-Paste):
| Scheme | Color Name | Hex Code |
|---|---|---|
| Monochromatic | Base Blue | #1E4299 |
| Tint (Lighter) | #6C8BC9 | |
| Shade (Darker) | #12285C | |
| Tone (Muted) | #4D5C7A | |
| Analogous | Yellow-Orange | #F9A602 |
| Yellow (Dominant) | #FFD900 | |
| Yellow-Green | #96C81E | |
| Complementary | Red | #D92121 |
| Green | #0CA52A | |
| Split-Complementary | Red | #D92121 |
| Yellow-Green | #96C81E | |
| Blue-Green | #138A72 | |
| Triadic | Red | #D92121 |
| Yellow | #FFD900 | |
| Blue | #1E4299 | |
| Tetradic (Rectangular) | Red | #D92121 |
| Green | #0CA52A | |
| Orange | #F26C0D | |
| Blue | #1E4299 | |
| Tetradic (Square) | Red | #D92121 |
| Yellow-Orange | #F9A602 | |
| Green | #0CA52A | |
| Blue-Violet | #493798 | |
| Achromatic | White | #FFFFFF |
| Light Grey | #CCCCCC | |
| Mid Grey | #777777 | |
| Black | #000000 |
